Target to eliminate excess production from steel, coal sectors will pose a major challenge in 2017
Editor's note: This is the fourth story in a series of previews on the two sessions-the annual gatherings of the nation's top legislature and its top body of political advisers. The sessions will start in early March.
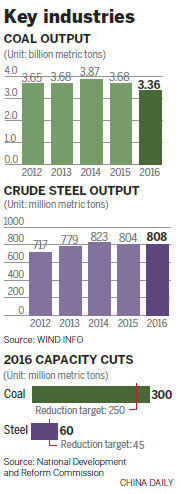
China will further reduce excessive steel and coal capacity this year, building on the progress it made in 2016, when it cut 45 million metric tons of steel and 250 million tons of coal.
The government will unveil its 2017 capacity reduction target soon, according to Xin Renzhou, deputy director of industrial policy for the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology.
The Government Work Report, to be presented by Premier Li Keqiang on Sunday, is also likely to review the efforts to eliminate excess capacity last year, he said.
Xin said supply-side structural reform will continue to be a priority for the steel sector - as well as a hot topic at this year's meetings of the National People's Congress, the top legislature, and the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, the top political advisory body - as the country presses ahead with major economic reforms amid downward pressure.
The mission to cut overcapacity in the steel and coal sectors remains a big challenge, he added.
By 2020, China aims to cut overall steel capacity by 150 million tons and coal capacity by 800 million tons, with most of that done by the end of this year.
The National Energy Administration earlier set a goal for the coal industry to cut capacity by 50 million tons, down by 80 percent on the 2016 target of 250 million tons.
State-owned enterprises managed by the central government have promised to cut excess steel and coal capacity by 5.95 million tons and 24.73 million tons respectively this year, according to the State-Owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission.
The government also plans to scrap 300 loss-making enterprises as well as 500 enterprises that have been in long-term difficulty.
Provincial governments have published capacity reduction targets, too, including Hebei, Shandong and Shanxi provinces and the Inner Mongolia autonomous region.
Hebei, for example, has said it will cut steel capacity by 31.86 million tons and coal capacity by 7.42 million tons as well as close four "zombie" enterprises, which are economically inviable businesses that survive only because of financing from governments or banks. Last year, Hebei cut about 33 million tons from its steel capacity.
"2017 will be our toughest year for capacity reduction," said Zhang Qingwei, the governor of Hebei, which produces one-fourth of China's iron and steel.
Xin said companies should focus on eliminating substandard steel.
Xu Lejiang, the vice-minister of industry and information technology, said at a recent news conference that China will not waver in its resolve nor slacken its efforts to implement the strategy.
To get steel companies to further cut capacity, the central government is encouraging them to sign long-term contracts with coal and downstream steel consumers while improving the quality of their products.
The measure, set out in a document issued by five ministry-level bodies, is aimed at stabilizing steel prices, which have seen fast increases of late, and further cutting industrial overcapacity.
Despite rises in the spot and future prices of steel in the short term and a recent recovery in output and sales, steel companies should make further efforts to cut capacity to support economic growth, according to a report by the National Development and Reform Commission, the top economic planner, and four ministries.
The report said China's oversupplied steel sector has seen years of plunging prices and factory shutdowns due to the sluggish economy.
Jiang Zhimin, president of the National Coal Industry Association, said the goal for the coal sector may look lower this year, but in reality the challenge is even more daunting.
"Unlike last year, when many mines were shut down and no longer producing, or were about to be closed, this year's capacity reduction target is aimed at a great number of coal mines that are still in operation," Jiang said.
Xu He contributed to this story.
Five target areas
Power: The central government has said it is essential to further reduce excess capacity in this sector. The average annual utilization rate of the nation's power-generation equipment fell last year to the lowest level since 1964.
The China Electricity Council has forecast that the growth rate in power consumption will decrease this year.
"Power enterprises will face an overall loss this year," according to Qiao Baoping, president of China Guodian Corp, one of the five major power enterprises. The company has pledged to reduce its investment in thermal power (it has canceled six projects) to cut production and increase investment in clean energy.
Nonferrous metals: China aims to cut surplus capacity of nonferrous metals like aluminum. In a plan drafted by the Ministry of Environmental Protection to tackle air pollution, one target is to cut the total aluminum production capacity in Hebei, Shandong, Henan and Shanxi provinces by 30 percent, 21st Century Economic Herald reported.
The four provinces account for one-third of the total national capacity. The main types of nonferrous metals are aluminum, copper, brass, silver and lead.
Oil refining: Like with steel and coal, growth in capacity in this sector has continuously outpaced growth in demand in China. Analysts expect the glut in refined fuels could last for years, partly because of the slowing demand domestically and a surfeit of refining capacity. Cutting overcapacity remains the biggest challenge for refiners, according to Li Li, director of energy research at Independent Chemical Information Service China. The nation has issued quotas of 81.93 million metric tons of crude oil to 22 refineries to tackle the problem.
The crude oil processing capacity reached 521 million tons in 2015, operating at only 75 percent of full capacity, well below the global operating rate, said Su Jun, a general manager at China National Petroleum Corp.
Cement: A fund is expected to be launched this year to encourage cement producers to cut capacity, as the nation attempts to reduce overcapacity in the building materials sector.
Kong Xiangzhong, head of the China Cement Association, told China Securities Journal the fund will be used to reward manufacturers that cut capacity. The industry, which faces a glut of supply and low market concentration, needs to explore market-oriented methods to carry out supply-side reform, Kong said.
Data from the National Bureau of Statistics show China produced 2.4 billion metric tons of cement last year, up by 2.5 percent on 2015. Yet the output from Beijing and nine other provincial regions decreased year-on-year.
Shipbuilding: The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology set out a plan in January to cut excess capacity and push industrial transformation in this sector.
It states that small and medium-sized shipyards that have low manufacturing skills and poor supervision should be weeded out, while competitive manufacturers should be encouraged to expand through reorganization or mergers and acquisitions.
Li Zhengjian, deputy secretary-general of the China Association of the National Shipbuilding Industry, said companies who do not meet safety and environmental standards or have high accident rates should be targeted in efforts to cut overcapacity.
Chongqing has said it is planning to cut capacity by 20,000 dead weight tons over the next three years.
Contact the writers at zhengxin@chinadaily.com.cn
