Trying to solve an aviation mystery
|
Bernard Decre believes the fliers aboard L'Oiseau Blanc attempted a sea landing as the plane was running out of fuel. The New York Times |
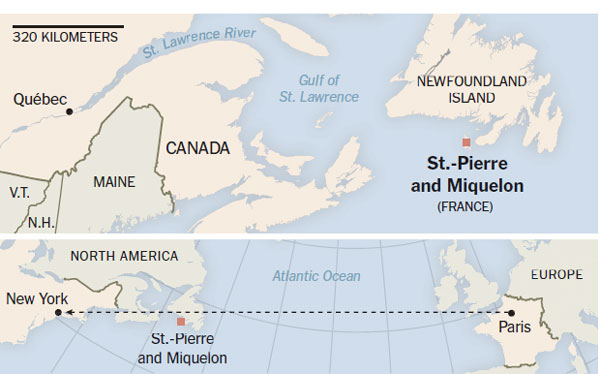
ST.-PIERRE - The disappearance of two French aviators attempting the first, near-unthinkable flight between Paris and New York in 1927 is considered one of aviation's great mysteries and has inspired decades of hypothesizing.
A growing body of evidence, however, suggests that the aviators crashed off the tiny island of St.-Pierre, about 15 kilometers from Newfoundland.
It is a theory championed by Bernard Decre, who has committed the past five years to a full-time search for their single-engine biplane, L'Oiseau Blanc, or The White Bird.
"We just want to recognize that they accomplished a fantastic crossing," said Mr. Decre, 73, an expert mariner and communications executive who is now retired.
A nonstop flight from Paris to Newfoundland would have been the first between Continental Europe and North America, and the first Atlantic crossing from east to west.
Mr. Decre believes the French fliers - Charles Nungesser, an aristocrat and flying ace, and Francois Coli, a one-eyed mariner - were forced off course by storms over Newfoundland. With fuel running low after about 35 hours, the men attempted a sea landing off St.-Pierre, he contends, amid a heavy, late-morning fog.
Mr. Decre began his investigation in 2007 after reading novelist Clive Cussler's account of his own search for the plane in Maine. Mr. Decre has since combed archives in France, Canada and Washington and come repeatedly to St.-Pierre.
He has found records showing that 13 people saw or heard the plane heading south along the eastern coast of Newfoundland on the morning of May 9, along with at least four residents of St.-Pierre. A local fisherman, no longer living, used to speak of hearing a plane crash and cries for help, Mr. Decre said.
Mr. Decre was in St.-Pierre in May, equipped with a powerful magnetometer and a multidirectional sonar unit. (With backing from the local authorities, the French government and especially Safran, the aerospace and defense company, Mr. Decre's budget this year reached about $200,000.) Three weeks of scans in about 55 meters of water turned up nothing, though.
St.-Pierre, despite its location, belongs to France. During Prohibition in America the island became a major hub for bootleggers, and it has been suggested that L'Oiseau Blanc was shot down by the United States Coast Guard, mistaking the French fliers for rumrunners.
At the National Archives in Washington, Mr. Decre found a Coast Guard telegram from August 1927 describing the apparent wreckage of a biplane wing floating off the Virginia coast. "It is suggested to headquarters that this may be the wreck of the Nungesser Coli airplane," it reads.
That sighting would be in keeping with a crash off St.-Pierre, said Mr. Decre, who means to continue his search.
The local populace is skeptical. Serge Perrin, 56, shucking scallops on his boat, said of Mr. Decre's quest, "We never heard anyone talk about L'Oiseau Blanc before he showed up."
The New York Times