Scientists shed light on crucial mechanism in tumor immune evasion

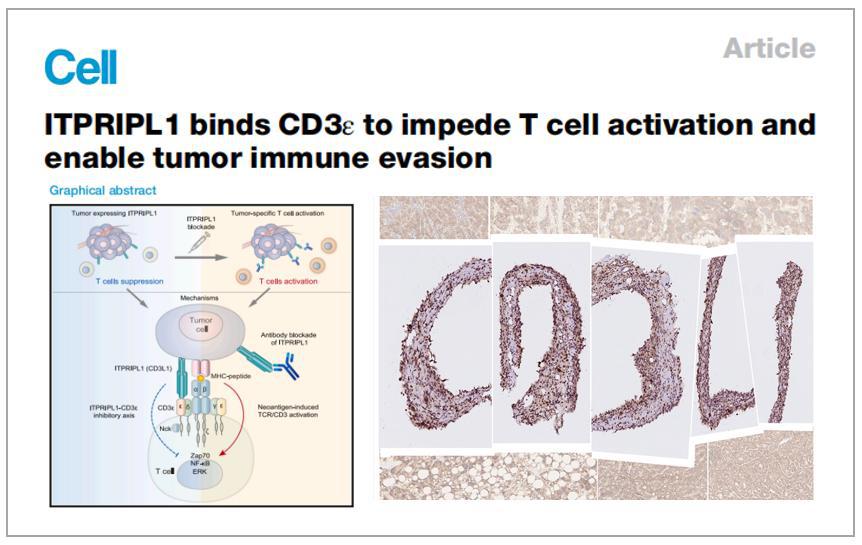
Scientists from the Institutes of Biomedical Sciences at Fudan University in Shanghai recently shed light on the gene CD3L1 in their research, revealing it as a crucial mechanism in tumor immune evasion, especially in patients who respond poorly to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory therapies.
Previously, PD-1/PD-L1 was one of the most widely used effective drug targets, but a large number of patients do not respond well to those immunotherapies.
A paper of the new research was published on the website of the journal "Cell" on Friday.
In the paper, the scientists said that the expression of CD3L1 exhibits several intriguing characteristics, including its mutual exclusivity with PD-L1 expression in most tumors, its prevalence in tumors resistant to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade, and enrichment in immune-privileged organs.
Such features suggest alternative immune evasion pathways and highlight the role of CD3L1 in maintaining immune privilege, they said.
They also found through knockout studies in mice that CD3L1 plays a pivotal role in maintaining immune privilege, as its absence led to substantial autoimmune reactions in the testis.
The CD3L1 antibody is currently in phase I clinical trials after obtaining investigational new drug approvals in both the United States and China. Its clinical trials for the treatment of multiple solid tumors in advanced stage are recruiting patients.
- Former Hainan official sentenced in bribery case
- Hangzhou residents enjoy rare snowfall
- Artificial reefs part of successful marine conservation efforts in Guangdong
- Zigong lantern festival combines cultural heritage with advanced technology
- Woman executed for abusing and killing stepdaughter
- Zhangjiakou academy students hit Olympic ski slopes as winter break begins





































