Dinosaur embryo study backs ancestral link to birds

A new study examining an embryo from a fossilized dinosaur egg has provided further evidence supporting the notion that modern birds evolved from dinosaurs.
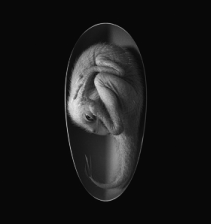
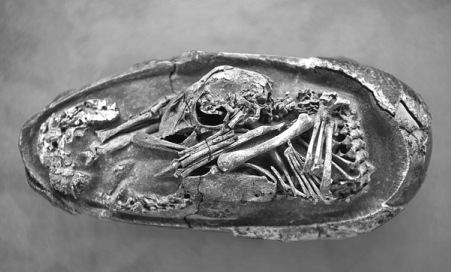
The embryo fossil was discovered in rocks in Ganzhou, Jiangxi province, around the year 2000 and is housed in the Yingliang Stone Nature History Museum in Fujian province, where it was dubbed "Baby Yingliang".
Estimated to be 27 centimeters from head to tail, the creature lies inside a 17-cm-long egg. Paleontologists believe it belongs to a toothless theropod dinosaur, or oviraptorosaur, dating back 72 to 66 million years, within the Cretaceous Period.
The posture of the embryo within the egg implies that these dinosaurs developed birdlike postures close to hatching, according to the study published in the journal iScience on Wednesday.
Scientists from China, Britain and Canada who worked on the study found the posture of "Baby Yingliang" unique among known dinosaur embryos-its head lies below the body, with the feet on either side and the back curled along the blunt end of the egg. Previously unrecognized in dinosaurs, this posture is similar to that of modern bird embryos.
Before hatching, birds are known to develop a series of tucking postures, bending their body and extending their head under their wings. Embryos that fail to attain such postures have a higher chance of death due to unsuccessful hatching.
By comparing "Baby Yingliang" with the embryos of other dinosaurs and birds, the research team proposed that such prehatching behavior, which was previously thought unique to birds, evolved in theropod dinosaurs tens or hundreds of millions of years ago.
Fion Waisum Ma, joint first author and PhD researcher at the University of Birmingham, said the dinosaur embryo study could help bolster people's understanding of dinosaur growth and reproduction.
"It is interesting to see this dinosaur embryo and a chicken embryo pose in a similar way inside the egg, which possibly indicates similar prehatching behaviors," Ma added.
Steve Brusatte from the University of Edinburgh, who is part of the research team, said this little prenatal dinosaur looks just like a baby bird curled up in its egg, providing yet "more evidence that many features of today's birds first evolved in their dinosaur ancestors".
Dinosaur embryos are some of the rarest fossils. To further test the hypothesis, more embryo fossil discoveries are needed, said coauthor Xing Lida, professor at the China University of Geosciences in Beijing.