Galbot banks on Sim2Real for expansion
Simulation-to-reality methodology a breakthrough by firm in cutting costs


As humanoid robots transition from product development to real-world commercialization and deployment, Beijing Galbot Co Ltd is working to crack the code to achieve scalable automation through a radical synthetic data approach.
In a recent exclusive interview with China Daily, Zhang Zhizheng, co-founder of Galbot, detailed how the company's simulation-to-reality, or Sim2Real, methodology is overcoming a critical industry barrier — the prohibitively high cost of real-world data collection.
The heart of Galbot's breakthrough lies in its pioneering technical paradigm — massive pre-training on a large scale and high-quality synthetic datasets followed by surgical fine-tuning with minimal real-world data. This innovative framework has drastically reduced reliance on real-world data collection.
Zhang said, "We've enabled skills mastered in virtual environments to seamlessly transfer into novel real-world contexts with minimal semantic relabeling."
This approach resolves the sector's persistent data scarcity crisis while dramatically enhancing training efficiency and generalization capabilities — establishing the essential groundwork for autonomous, general-purpose robots.
Founded in 2023, Galbot has already raised 2.4 billion yuan ($334.8 million) from big-name investors such as battery-making giant Contemporary Amperex Technology Co Ltd.
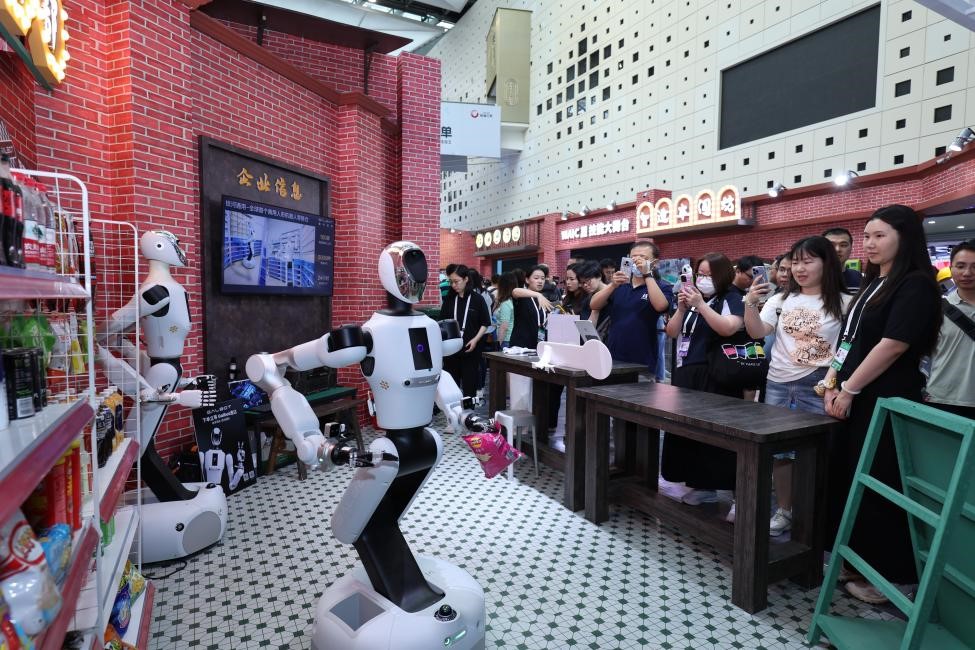
Today, Galbot's humanoid robots are already operating autonomously in over 10 pharmacies in Beijing, performing complex tasks like retrieving medicines from crowded shelves and delivering orders to night-shift couriers — all without human intervention.
"We plan to open 100 such stores nationwide by the end of this year," Zhang said.
At the same time, the company's industrial expansion is being accelerated through its joint venture with a Bosch unit.
"Galbot's systems are engineered to meet stringent industrial requirements where failure is not an option. Factories demand unwavering accuracy between 99.9 percent and 99.99 percent," he said, adding that this necessitates billions of data points to achieve robust generalization.
The company is partnering with Germany's Bosch to deploy humanoid robots in factories. The JV will focus on applying embodied AI in high-precision manufacturing, such as complex assembly, aiming to drive large-scale industrial deployment of embodied AI.
"I believe a commercial rollout of humanoid robots in factories is achievable within two years," Zhang said.
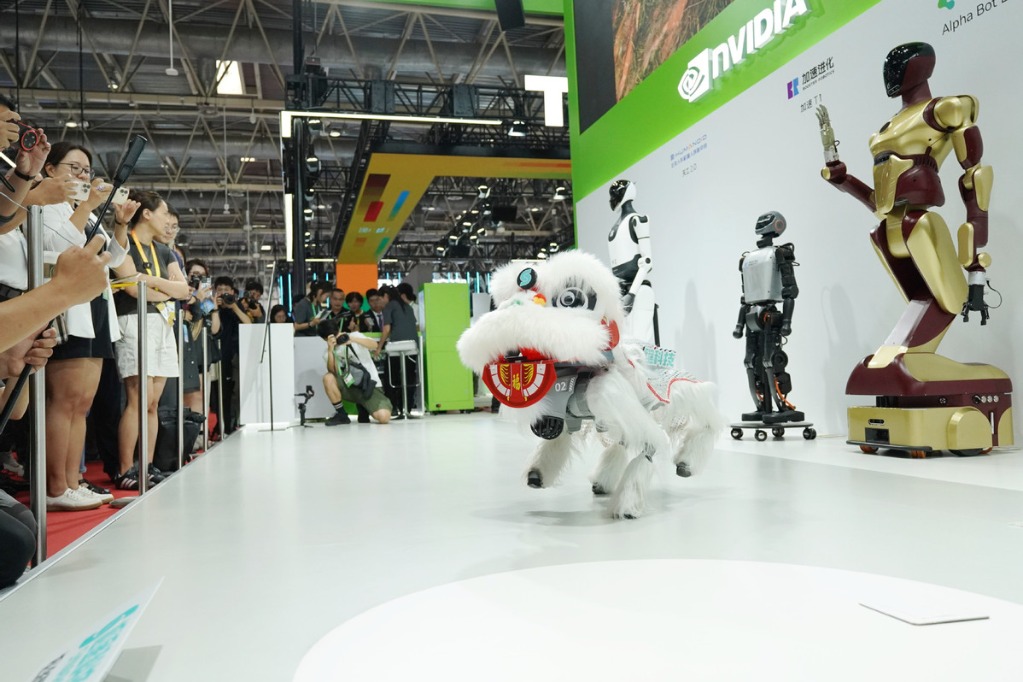
At the 2025 World AI Conference in Shanghai in July, Galbot's robots performed live demonstrations, proving their operational maturity beyond the conceptual stage. Within a reconstructed supermarket environment designed to replicate real-world complexity, a robot executed unified cross-category handling, grasping diverse items such as soft potato chip bags and rigid bottles among cluttered shelves without preprogrammed pathways.
China's humanoid robot market is expected to grow into a more than 100 billion yuan ($13.6 billion) market by 2030, up from 2.76 billion yuan in 2024, according to a report from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology.
Goldman Sachs Research predicts the global humanoid robot market could hit $154 billion by 2035, with optimistic projections reaching $205 billion.
Xie Shaofeng, chief engineer of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, said at a news conference that the ministry has also coordinated with provincial governments to develop 11 national AI innovation pilot zones.
Meanwhile, central and local authorities have jointly built specialized manufacturing innovation centers for embodied AI robots, humanoid robots and other next-generation technologies to drive the development of industrial clusters, Xie said.
masi@chinadaily.com.cn