Yungang Grottoes in urgent need of attention
Updated: 2008-01-02 21:23
The grottoes were included on the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization World Cultural Heritage List in 2001.
Hundreds of thousands of visitors come to pay their tributes every year, but few of them are concerned or have even noticed the gradual decay of the Buddha images.
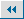
Many of the statues' surfaces have flaked off as they have weathered, and some of their faces have been completely worn away, Wen Xiaolong, a researcher from the institute, said.
"The sandstone has become very crisp, and it will slake off upon a light touch or stroke," Wen said.
Water penetration is a major natural destroyer of the grottoes, said Director Yuan Jinghu. With the downpours directly washing their bodies, and the accumulated water eating out their basements, the statues suffer the most serious erosion in July, August and September, when large quantities of rainfall hit the region.
But weather is not the only source of the damage. Datong, the city where the statues sit, is a longtime industrial city famous for its coal production.
The floating coal dust, mixed with the sulfur dioxide produced from coal burning, are two more culprits behind the statues' decay.
"The combination of the dust and gas brings fatal chemical reactions to the sandstone statues," Yuan said.
Although the government has allocated over one hundred million yuan for the construction of a new coal transport route far from the Yungang Grottoes and a large annual sum to maintain the grottoes, there is still another threat, in the form of increasing numbers of tourists.
"Besides the intentional infringements, such as littering and excessive touching or improper climbing, the carbon dioxide that humans breathe out is also corrosive to the statues," the director said.
Yuan is concerned for the future of the statues, and said that as humans, visitors should understand and respect the statues' importance.
"The statues have lives like human beings, and if we protect them, they will live. If not, they will die, and later generations will never have the chance to encounter such glorious art," Yuan said.
|
|
|
||
|
||
|
|
|
|