Full-blown economic crisis unlikely in China
Updated: 2011-09-30 09:33
By Li Xiang (China Daily)
|
|||||||||||
BEIJING - A global recession could be the biggest risk facing China, but a full-blown economic crisis is unlikely, given the nation's relatively healthy balance sheets, said Huang Yiping, chief economist of emerging Asia at Barclays Capital, the investment banking arm of Barclays PLC, on Thursday.
"A global economic recession could cause a hard landing for the Chinese economy because of its high dependency on trade and limited policy flexibility," Huang said.
According to a recent survey by the British investment bank, a hard landing in China is viewed by investors as the third-biggest downside risk to emerging markets assets in the coming three months.
Although China has a number of homegrown problems, such as extraordinary credit expansion, an overheated property market and difficulties in local government financing, Huang said growth is likely to remain robust despite the external uncertainty.
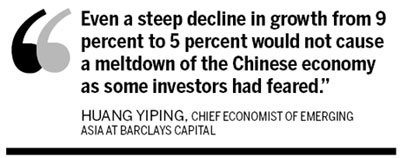
Barclays Capital forecast that Chinese economic growth will be 9.1 percent in 2011 and 8.4 percent in 2012. "Even a steep decline in growth from 9 percent to 5 percent would not cause a meltdown of the Chinese economy as some investors had feared," Huang said.
Huang noted that the country's strong balance sheet, backed by foreign exchange reserves of $3.2 trillion, a current account surplus of around 5 percent of GDP and a strong currency, will give the government enough room to stretch policy and prevent a systemic economic meltdown.
"Chinese households are not highly leveraged," he said. "And the banks in general remain in robust financial health, with an average non-performing loan ratio of 2.5 percent, which provides them with enough room to absorb any rise in bad loans in the coming years."
Meanwhile, economists expect that the central bank will keep the benchmark interest rate and reserve-requirement ratio unchanged for the rest of the year until a clear judgment is made on the macroeconomic risks. The consumer price index, a main gauge of inflation, dropped from 6.5 percent year-on-year to 6.2 percent in August, mainly due to the base effect.
"The cycle of monetary tightening is likely to come to an end, although the upside risk of inflation cannot be ruled out," Huang said. "So we believe the government's monetary policy stance is in a 'wait and see' mode."
Industrial production, fixed-asset investment and retail sales all slowed moderately in August, which is consistent with market expectations.
"Activity indicators are slowing, but not sharply. These add further confidence to the notion that China is experiencing a soft economic landing," said Zhang Zhiwei, chief China economist at Nomura Securities Co Ltd, in a report.
Related Stories
China pledges no economic hard-landing 2011-08-19 16:30
China's hard-landing fear unnecessary: Expert 2011-07-26 14:33
GDP growth eases fears of hard landing 2011-07-14 09:28
Hard landing not likely for China 2011-07-08 16:11
- Tight electricity supply to return during winter
- China makes moves to increase imports
- Full-blown economic crisis unlikely
- Bumper crop, but price still rising
- Holiday to be boon for places overseas
- Sinohydro raises 13.5b yuan in IPO
- China expands lending to fund-hungry small firms
- '9% GDP growth' for 2011













