Conservation lifts delicate ecosystem


"One example is our innovative 'Life Bird's Nest' project — we install artificial nests in safe locations on power transmission towers. This guides birds to nest and breed away from live electrical components, effectively solving the global challenge of balancing grid development with bird conservation," Hou says.
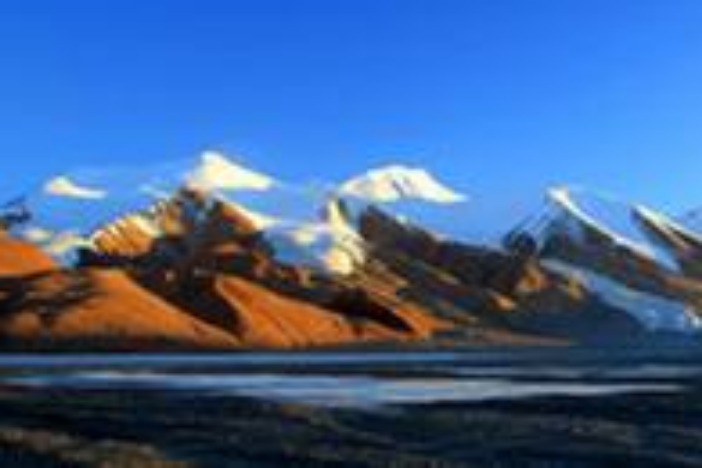
The population of Tibetan antelope has grown from fewer than 20,000 at the start of conservation efforts in 2000 to over 70,000 today. The number of snow leopards monitored in the province has also surpassed 1,200.
At the Qinghai Lake Biodiversity Conservation Research Center, lively Przewalski's gazelles gracefully bound across the windswept grasslands, their hooves barely making a sound on the soft earth. Visitors watch in quiet awe as the herd pauses intermittently, noses twitching in the crisp mountain air and ears flicking at distant calls.
Huang Zhuomojie, an ecological caretaker at the center, explains: "Przewalski's gazelles are part of a rescued population. Some were strays found around the area while others were injured. Initially, we rescued two but today, nearly 80 roam here freely.
"This area serves as an important corridor for gene flow between wild Przewalski's gazelle populations. Through scientific research and genetic lineage management, the ultimate goal is to combine captive breeding with successful releases back into the wild," Huang says.
The population of Przewalski's gazelles dropped to just over 300 in the 1990s. Thanks to two decades of tireless conservation efforts, the Qinghai Lake region is now home to more than 3,400 Przewalski's gazelles, including wild populations.
"One of their distinctive features is their white rump. It's not just for decoration. Normally, it's inconspicuous, but when danger approaches, they raise their tails and the white fur flares up like a signal. This alerts the herd to flee," Huang says.
"Their activity range is relatively fixed, as they are non-migratory with home ranges of around 200 square kilometers. Using drones and other technologies, the research center monitors their habits and breeding patterns to provide them with better protection."