The age of restoration

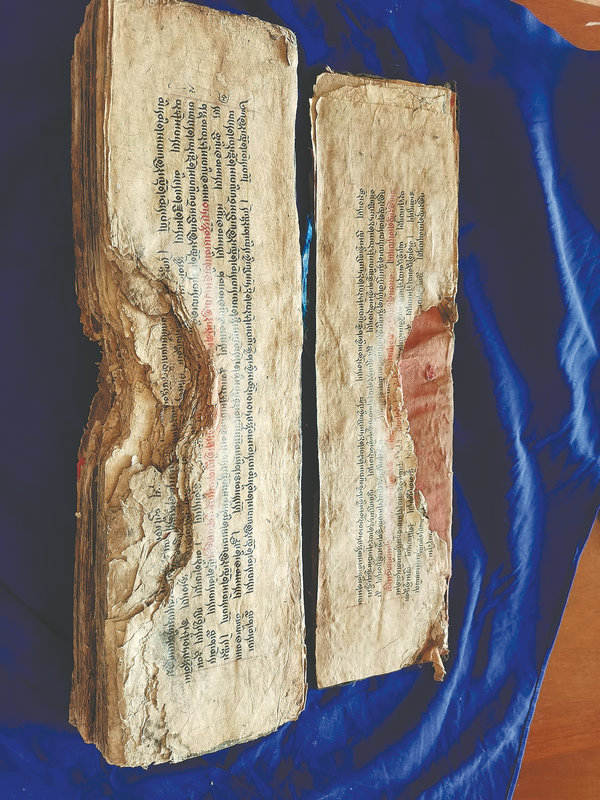
Separating the pages is another difficult part of the work. As scriptures are often unearthed from the debris of ancient monasteries, the pages are often stuck together. The scriptures resemble bricks.
The pages need to be separated using tools such as tweezers, screwdrivers and pins. In 2017, Yangla and Tseyang were invited to help the Trachilma chapel in Tibet's eastern Chamdo city to separate ancient documents. Five people from their center spent five days working on the separation of 480 woven bags of ancient documents.
The relics had remained untouched for 37 years since they were first unearthed in 1980.
"The majority of these unearthed ancient scriptures were written with gold ink. More than 30 people, including the monks, were involved in the work of separating the scriptures," says Tseyang.
"We were only able to separate about 50 bags worth of readable pages in the end. It was really hard to separate them, as the gold ink had stuck together," says Tseyang.
Yangla says that when her team was chosen to help the monastery to restore their ancient documents, none of them felt reluctant, despite the risk to their health.
"As these ancient scriptures had been sitting for 37 years, there was a large amount of mold on them, and the N95 masks did not work. Part of our faces and mouths became red and swollen due to the mildew on the scriptures," says Yangla.
"The head of the county was impressed by our work spirit, and he also came to help," she says.
The only measures Yangla and Tseyang had to protect themselves were a blue uniform and a mask. However, they never complained.
As a transparent plate is always required while preserving a page of ancient text, their eyesight has suffered, but they say it's worth it.
"The more we deal with this work, the more we love it and find it fulfilling," says Tseyang.
Over the past few years, their center has restored more than 5,000 pages of rare ancient Tibetan scriptures. The restoration of these works is entrusted by just a few monasteries in the region, including Pula, Mangra in Maldrogungkar county, and the Chayul Padkar Monastery of Lhunze county.
Each restored page of the scriptures has been preserved in the library with a specified file, according to the center.
"The file includes the photos of the repaired pages before and after the restoration, dates, the degree of damage, the reasons for the damage, and restoration plans," says Yangla.
"It's very important to make a file for each restored page. In the future, we can see what we have done, and the work will be easy to track and follow," says Tseyang.





































