HK awaits first organic waste treatment facility
Updated: 2016-02-18 08:26
By Timothy Chui in Hong Kong(HK Edition)
|
|||||||
Long-delayed plant will only process 6% of daily total even at capacity
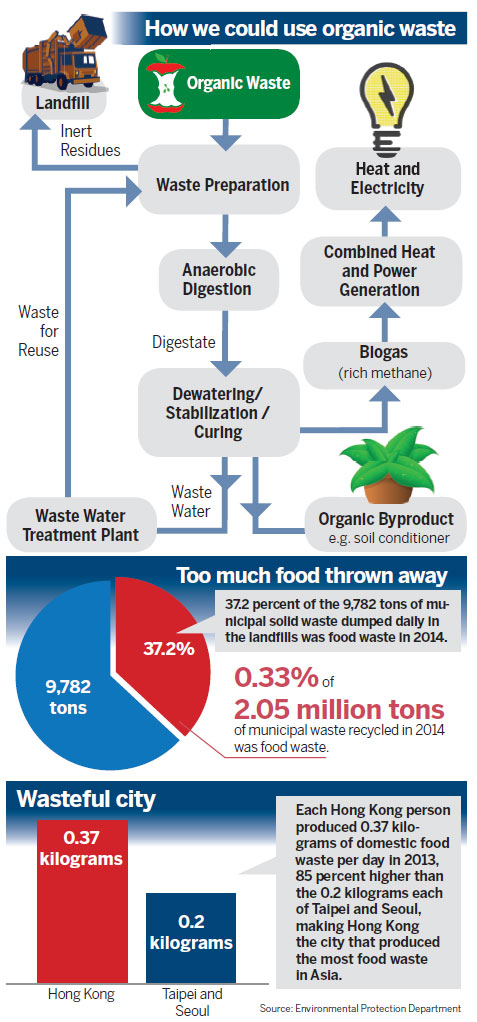
Efforts to divert organic waste from landfills have long been falling short in Hong Kong. Land scarcity and difficulties exporting waste to the mainland have left little room for disposing of it other than through landfills.
But things may be about to change for the better. Hong Kong's first organic waste treatment facility is expected to open in North Lantau by the middle of next year. It will be able to process about 200 metric tons of organic waste a day into biogas and fertilizers.
The treatment facility will begin operations four years late due to planning delays. It will handle 40 tons of waste from wet markets, while 160 tons in spare capacity are expected to be handled by the private sector on a daily basis.
Operating at capacity, the plant will handle less than 6 percent of the more than 3,200 tons of organic waste entering the city's landfills daily.
Planning for greater capacity is likely to begin in earnest. Greeners Action Executive Director Angus Ho said the city's landfills were fast reaching full capacity. He explained that efforts to construct incinerators were being slowed by judicial challenges and protests.
The same barriers to progress are threatening the development of more organic waste treatment plants. An Environmental Protection Department (EPD) source told China Daily that any future plants were still 15 years away.
The goal to build five to six plants with a total capacity of 1,500 tons per day seems lofty. The source explained that a lot of time was needed to find suitable sites. The approval of environmental impact analysis and legislative support also had to be secured.
Steering organic waste away from landfills and into recoverable products would substantially reduce the amount of garbage going underground. Nearly 10,000 tons of municipal solid waste is derived from domestic, commercial and industrial sources.
This excludes construction-related waste entering landfills every day in 2014. Just under a third, or 3,260 tons, of the rubbish is made up of food and other organic waste.
The government has already missed a target to have only 25 percent of municipal solid waste disposed of at landfills by 2014.
Small-scale pilot programs supported with government grants are already operating. Moreover, source separation of organics is already commonplace in much of the developed world.
tim@chinadailyhk.com
(HK Edition 02/18/2016 page8)