Inflation a real threat for less privileged
By Wang Lan (China Daily)Updated: 2007-06-28 17:11
|
People buy fresh pork at a supermarket in Zhengzhou, capital of Central China's Henan Province. The price of pork has risen sharply over the past couple of months, contributing to rise in the consumer price index. [newsphoto] |
To understand their worries, it's important to recognize the driving force behind the current round of inflation: rising food prices. As such, the traditional weapon against inflation has proved mostly ineffectual - because the inelastic demand for food is insensitive to all monetary measures.
Contrary to popular belief, raising the interest rate and other measures to tighten liquidity won't check inflation because the CPI is driven largely by consumers' demand for food rather than the aggregate demand of society. In fact, such measures could even increase inflationary pressure by raising the cost of doing business in China.
A slight rise in the CPI above 3 percent, generally accepted as the starting point of inflation, may not be felt much in the urban areas. But underprivileged people living in less developed areas know what it means. For instance, life for jobless laborers in Jiamusi has become even more difficult after the rise in food prices. That's because a family of three in the medium-sized city of Northeast China's Heilongjiang Province can get only up to 500 yuan a month as unemployment benefit.
"We have to cut our daily consumption of pork and eggs. An extra 8-10 yuan for a kg of pork make a lot of difference for my family. It makes our life more difficult," says a laid-off worker. In the past two months, the price of pork in Jiamusi has jumped 58 percent to 20 yuan a kg, and soybean oil costs 28 percent more that it did a year ago.
It's not that people in big cities such as Shanghai don't feel the pinch. Many people in the country's commercial capital are making long trips to wholesale markets because they can buy foodstuff and other products at 10-20 percent less than what they have to pay in neighborhood shops. "The money we save is worth the extra effort," says a middle-aged woman. Lower prices are not enough for her because she visits the market late in the day to avail of all the possible discounts.
More cautious shoppers, and those who can afford it, have no option but to increase their spending on food products. Britain-based TESCOLegou, one of the world's biggest retailers, has raised prices of food products in all its 17 supermarkets in Shanghai from April. Among the six major food products that are costlier are pork (30 percent more), eggs (15 percent), grains and edible oil (about 10 percent). "We have raised prices of food products in proportion to the increase in our purchase prices," says TESCOLegou purchase department employee Tang Tian.
Higher food prices have hurt hotels and restaurants, too. "The prices of the main ingredients in our buffet meals have risen. But we have to bear the extra cost because we cannot raise the prices," says Shenzhen-based Pavilion Hotel staff Nancy Zhang. The reason is simple: raise prices and lose customers.| 1 | 2 | 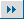 |
(For more biz stories, please visit Industry Updates)

