Producing China's engineers of the future


Upgrading the nation's manufacturing sector will require innovative steps to cultivate new talent. Cheng Si reports.
In a modern skyscraper, even a tiny screw or brick is of vital importance, and the same is true of the skilled workers who tighten the last screw in strict accordance with the architect's plan to build a safe, solid shelter.
In China, skilled technicians and engineers, even those recognized as having a high level of competence, were once plagued by low social status, poor conditions and meager salaries. Gradually, though, they have earned respect, in tandem with the rise of the manufacturing sector.
"Highly skilled workers were first classified by the government in 2003. In 2015, they were included as one of the major State-level talent groups, along with theoretical scientists, technological leaders and entrepreneurs, marking a significant rise in their social status," Zhang Lixin, director of the Vocational Capacity-building Department at the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security, said at a news conference in December.
He said that by the end of last year, the skilled labor force had risen to more than 165 million, with those classified as highly skilled reaching nearly 48 million. The numbers signaled rises of 23 percent and 39.3 percent respectively from 2012.
He Liangping, dean of Yunnan Technician College in Kunming, capital of the southwestern province of Yunnan, said: "The driving force of China's economic and social development has been transformed from labor-intensive industries to quality talent. Against that backdrop, this vast group of skilled workers is key to the nation's future development."
In addition, vocational education and skills training play a key role in improving workers' performance and making the nation a manufacturing power, he said.
Training upgrade
China's earliest modern skills training can be traced to the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911), when the Foochow Shipbuilding Institution in Fujian province was established in 1866, Minister of Education Chen Baosheng told a news conference last year.
However, vocational education lagged behind ordinary high school education before late leader Deng Xiaoping called for the development of more technical schools in 1978, when the adoption of the reform and opening-up policy highlighted a shortage of talented technicians.
As a result, the number of students at vocational institutes rose to more than 4.2 million in 1985, and the number of technical colleges rose by 4.6 percent.
By 1996, vocational students accounted for 56.4 percent of the total in high school education, an all-time record, according to the Chinese Society of Vocational and Technical Education.
More recently, technical education has received greater support from the central government to help shape the nation's manufacturing power. In 2014, the State Council, China's Cabinet, issued a guideline to make modern vocational education more open-minded and flexible as a way of delivering more skilled talent.
Last month, the Ministry of Education issued a plan to reform vocational education and produce high-quality technicians for 10 sectors in urgent need, such as agriculture and manufacturing.
"I was unwilling to send my son to a technical school because of the low social status of skilled workers," said Shao Qian, a 45-year-old from Henan province.
"I thought it would be better for him to attend an average higher education college than become an apprentice in a factory, but I changed my opinion when he won the first prize for welding at the technical college. I discovered things were not that bad; at least, he has mastered a skill that will help him earn a living. I think things will improve because the nation is making efforts to improve the economic and social treatment of skilled workers."
- Man sentenced to death for killing his children
- Hemodialysis services cover all counties with over 100,000 permanent residents
- Flu cases fall to moderate level
- Taiwan lawmakers vote to pass motion to impeach island's leader Lai Ching-te
- Remains of former senior Chinese legislator Peng Peiyun cremated
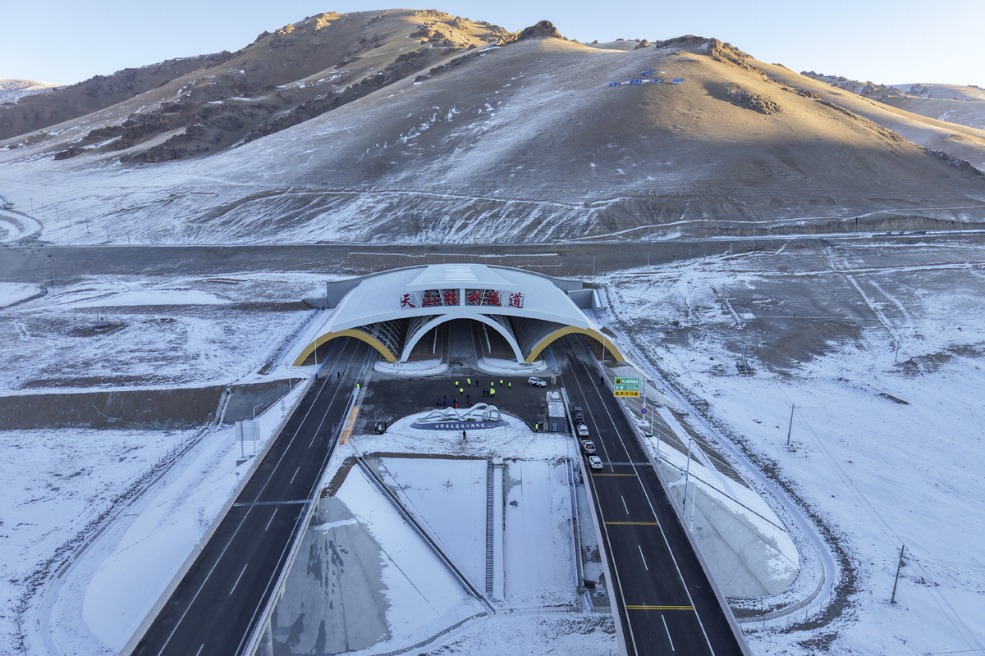
- World's longest expressway tunnel opens to traffic in Xinjiang