August 12, 1954, Hong Kong
EDUCATION:
1974-77: Bristol Polytechnic (now the University of the West of England), major in valuation and estate management
CAREER:
1983: Partner at Jones Lang LaSalle; president of the Hong Kong Institute of Surveyors; consultant to the steering group for Shanghai Pudong development; consultant to the steering group for Shanghai land-use reform; consultant to the steering group for Shenzhen land-use reform
1988: Secretary-general of the Basic Law Consultative Committee
1992: Hong Kong affairs consultant to the State Council's Hong Kong and Macao Affairs Office and Xinhua News Agency's Hong Kong branch
1993: Member of the Preparatory Committee for the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region
1996: Lawmaker of the Provisional Legislative Council
1997-2011: Executive Council convener for three consecutive terms
2012-17: Hong Kong SAR chief executive
2017-present: Vice-chairman of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference
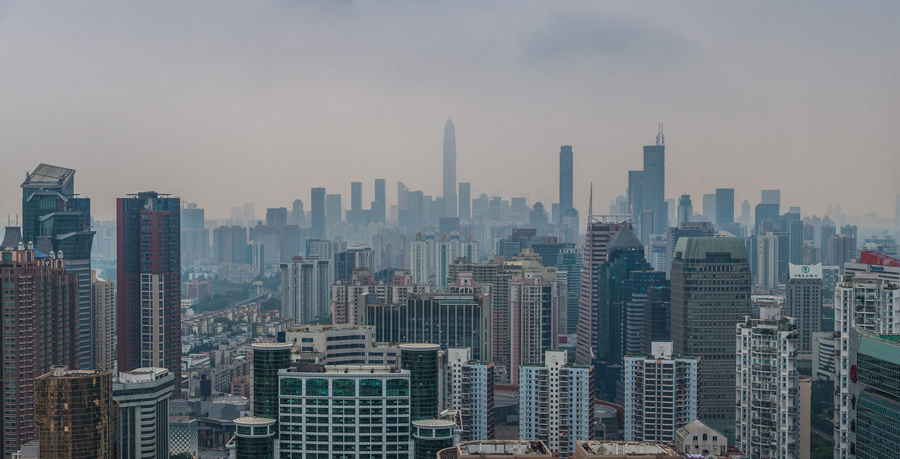
Hong Kong's changing role in China's transformation

A call to follow
Leung wove his early life into the fabric of the reform and opening-up policy. He dedicated himself to becoming a contributor in 1979, after graduating from Bristol Polytechnic (now the University of the West of England). Leung's studies led him into a career as a land surveyor.
"I followed what the country told me to," he said.
Leung's efforts put him on the front line of Shenzhen's early development. He also played a role when Shanghai embarked on China's first urban land reform in the 1980s.
There was no pay, no remuneration. Occasionally he would get some grain coupons, a replacement for cash that could be used to buy certain foods on the Chinese mainland from the 1950s to 1993.
"Now looking back, I found the experience interesting and meaningful," Leung said. He acknowledged that his involvement in the country's urban land reform proved one of the two most important turning points of his life.
Leung gained expertise in valuation and estate management, much of it from working on Shenzhen's urban plan. He was invited to share that expertise and his knowledge of Hong Kong's land policy with Shanghai officials in June 1987.
He gave a one-hour presentation, but when he was getting ready to go he thought of something else. "We just discussed theories. What if problems occur putting theories into practice?" Leung recalled asking the local officials. "It was Shanghai's first time in land leasing."
Leung persuaded the Shanghai government to send three officials to Hong Kong in early 1988. Together, they set up in a low-budget hotel, writing out by hand the tendering documents for China's first international land lease. In addition to compiling the lease document, Leung also translated it into English.
"We had no access to the internet, nor would we use a computer to type. We called Shanghai officials to inform them of the contents and amended the documents according to their suggestions," he said.
"It was energy-consuming. But I told the Shanghai officials that we were writing more than bidding documents. We were writing history."
It took the group 20 days to finish the tendering document. The last working day saw just two paragraphs left to be translated into English. Leung invited the team to go on a Spring Festival shopping spree. He was surprised when the three Shanghai officials declined.
"They said they would not leave until the work was finished," he said. "And in the end they didn't do any shopping.
"It struck me the most. Our country became strong for a reason. People, like the team I worked with, are committed to the country and to working diligently toward progress. That is part of the reason."
On March 22, 1988, Shanghai settled the nation's first international tenders for a land lease. A 1.29-hectare plot in the city's Hongqiao district was leased to a Japanese real estate developer, marking the opening of China's land-lease market to the international community.